Are you wondering how warehouses help make supply chains smoother? Warehouses boost efficiency by organizing inventory, speeding up order fulfillment, and reducing transportation costs.
Warehouses improve supply chain efficiency by storing goods close to customers or production lines. They use optimized layouts, such as stacking racks and automated systems, to speed up receiving, storage, and dispatching. This reduces delays and prevents stockouts, ensuring a smooth flow of goods from suppliers to consumers.
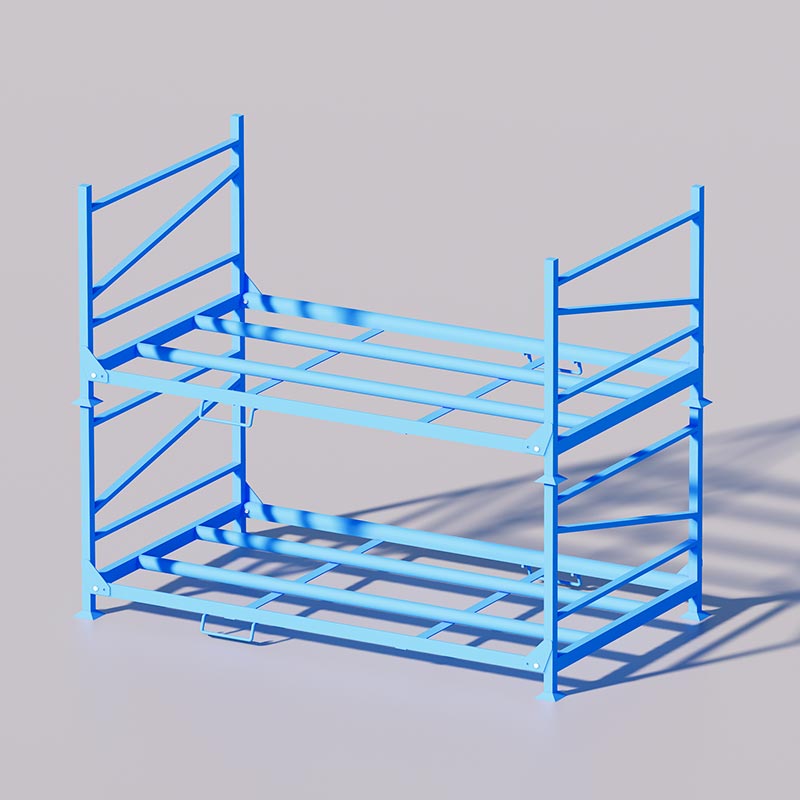
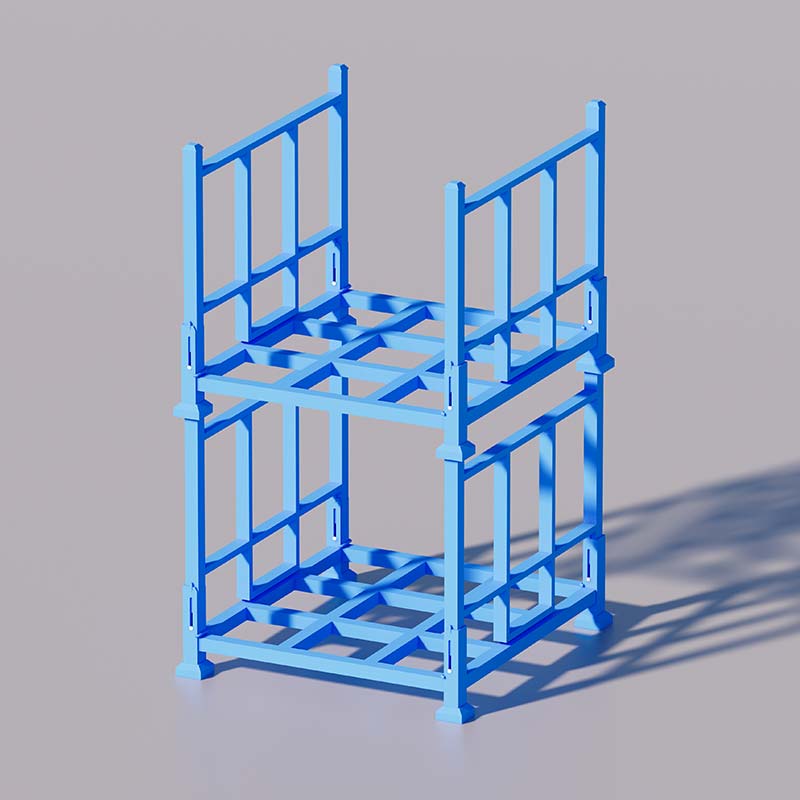
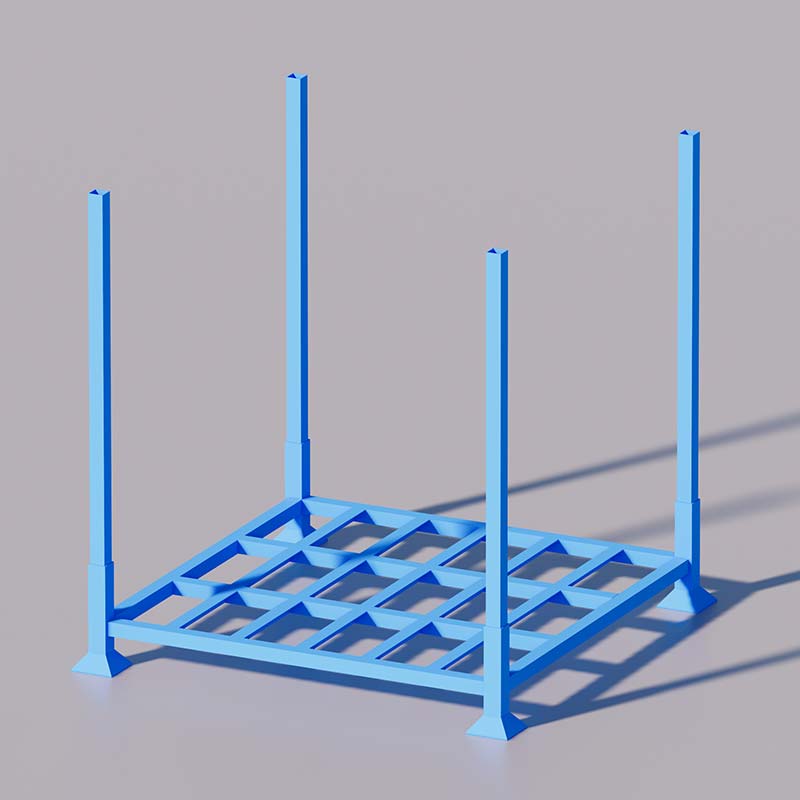
In warehouses requiring high-density storage, such as those storing cold storage goods, fabric rolls, tires, and palletized goods, stacking racks can be used to increase warehouse capacity. This not only significantly improves warehouse utilization and speeds up turnover efficiency but also reduces labor and material costs.
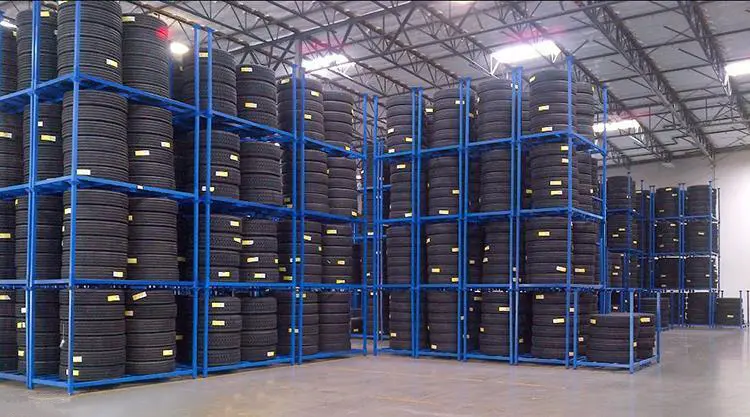

In addition, warehouses employ technology like warehouse management systems (WMS) to track inventory precisely. This minimizes errors and allows quick replenishment. Proper inventory control reduces excess stock and prevents shortages, speeding up delivery times. Strategic location also cuts down transportation time and costs, making supply chains more responsive and cost-effective.
What Safety Standards and Regulations Apply to Warehouses?
Warehouses must adhere to safety standards to protect workers and goods. These include OSHA regulations in the U.S., ISO standards worldwide, and local building codes.
Key safety regulations focus on fire prevention, proper storage practices, equipment safety, and employee training. Fire safety measures include sprinkler systems, fire extinguishers, clear escape routes, and regular drills. Heavy equipment like forklifts must meet safety standards, including operator training and regular maintenance. Storage systems such as racks must be designed to support loads safely and prevent collapses.
Regular inspections, employee safety training, and proper signage are also required. For warehouses handling hazardous materials, additional regulations ensure safe storage and handling. Compliance not only keeps workers safe but also avoids costly penalties and operational disruptions.
What's the Difference Between a Factory and a Warehouse?
A factory is for producing goods; it uses machinery, assembly lines, and high power to make products. In contrast, a warehouse is for storing goods—it uses shelves and forklifts to manage inventory before delivery.
Factories require heavy-duty infrastructure like reinforced floors and high-capacity electrical systems. They are dynamic spaces with ongoing production, often needing specialized zones for assembly, packaging, and quality control. Warehouses are more about organization and logistics, with open spaces and storage racks to handle large volumes of stock.
Interestingly, some facilities switch roles: when inventory is high, a factory space might become a temporary warehouse, using stacking racks to store goods.
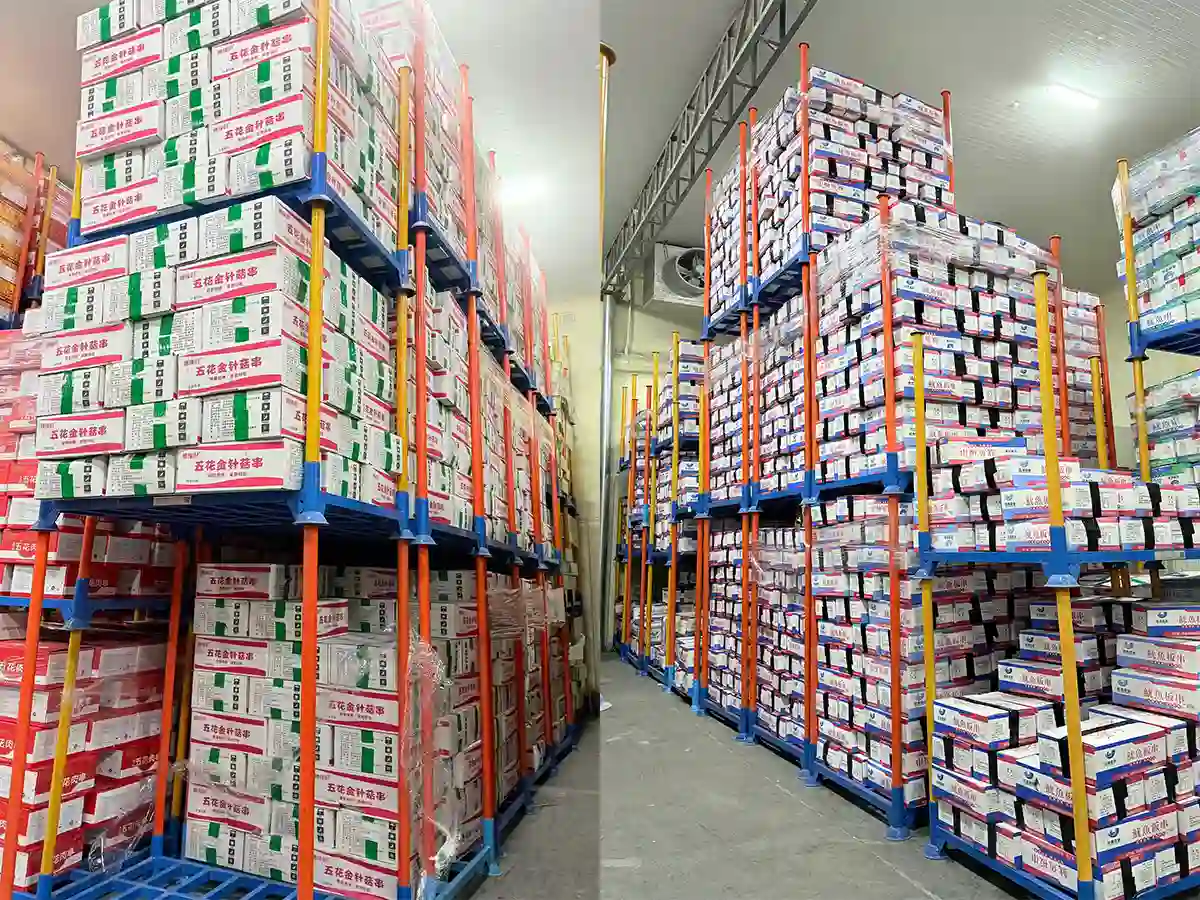

When production ramps up, those racks can be dismantled or folded to free space for manufacturing, and new inventory can be stacked efficiently. This flexibility highlights how stacking racks support both storage and production needs without fixed foundations.
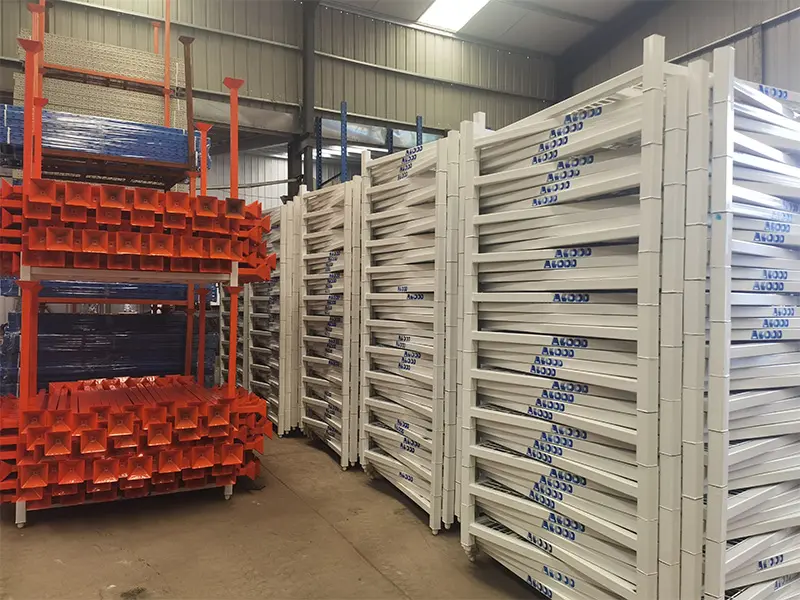

In summary, while factories make products, warehouses hold and manage inventory. But with adaptable stacking solutions, these distinctions can blur, creating versatile spaces that serve multiple functions.